The “GrassCall” malware campaign represents an advanced social engineering attack carried out by a Russian-speaking cyber-criminal organization referred to as “Crazy Evil,” with its subgroup “kevland” leading the operation. The campaign specifically targets job seekers in the cryptocurrency and Web3 sectors, using fake job interview schemes to compromise victims’ systems and steal their cryptocurrency assets.
Hundreds of people have been impacted by the scam, with some reporting having their wallets drained in the attacks.
Overview of Threat Actor behind it:
Crazy Evil” is a Russian-speaking cybercriminal organization that has rapidly evolved since its inception in 2021, becoming one of the most prolific groups targeting digital assets. The group specializes in identity fraud, cryptocurrency theft, and the deployment of information-stealing malware. Their operations are characterized by sophisticated social engineering tactics, often involving the use of “traffers”—social engineering experts who redirect legitimate traffic to malicious phishing pages.
Infection Chain:
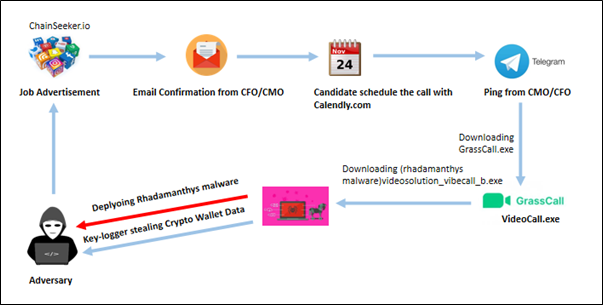
Attack Tactics and Approach:
Impersonating a Fake Company: The attackers set up a fabricated business, such as “ChainSeeker.io,” featuring a professional website and active social media accounts on platforms like LinkedIn and X (previously Twitter). They publish high-quality job advertisements on reputable job boards like LinkedIn, Well-found, and Crypto Jobs List to attract unsuspecting applicants.
Job Advertisement over social media platform:
Phishing Communication: Whenever interested Candidates responding to the job postings over social media, they have received emails inviting them to interview with senior company officials, such as the Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) or Chief Finance officer (CFO) over the mail. The conversation then transitions to Telegram, where the impersonated CMO/CFO provides further directions.
Mail received after applying to the Job posted:
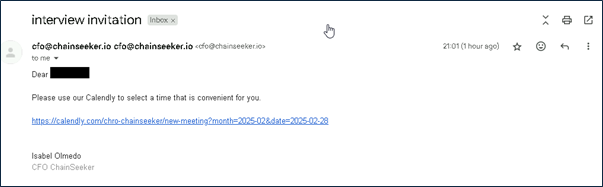
The conversation transitions to Telegram, where candidates are invited to schedule a call using Calendly, allowing them to select a suitable time slot.
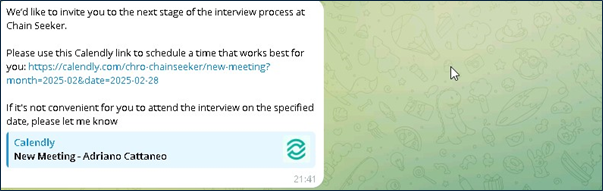
After candidates schedule their call within the chosen time frame, the CMO or CFO will reach out to them beforehand to provide additional details.
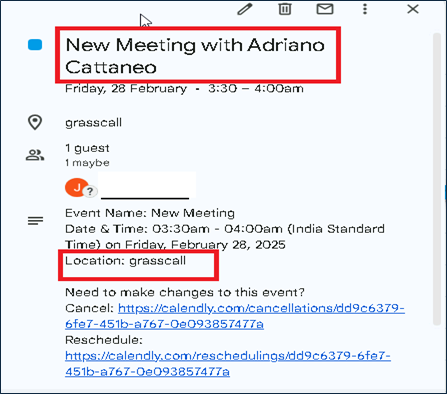
Just before the call their CFO/CMO contacting the candidate to join the call with shared passcode.
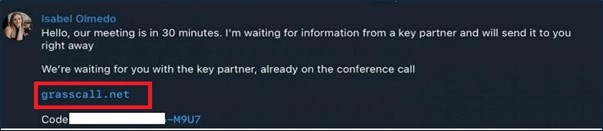
Malicious Software Deployment: The fake CMO directs candidates to download a video conferencing application named “GrassCall” from a specific website (e.g., “grasscall[.]net”). Access to the download requires a code provided during the Telegram conversation. The website detects the visitor’s operating system and offers the corresponding malicious client:
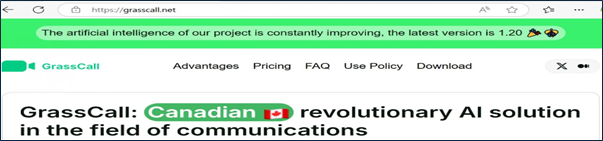
In our ongoing research recently, we have identified that adversary has rebranded their platform with https://vibecall[.]app/.
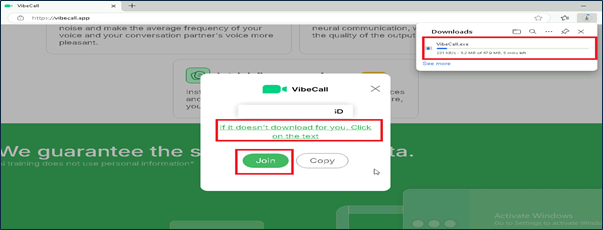
Here once candidate entered their passcode to join meeting GrassCall.exe will be downloaded based on OS.
Windows Users: Installing “GrassCall.exe” triggers the deployment of a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) combined with an information-stealing program like Rhadamanthys. These malicious tools enable attackers to maintain ongoing access, log keystrokes, and extract sensitive data, including cryptocurrency wallet credentials.
Mac Users: Installing “GrassCall_v.6.10.dmg” results in the activation of the Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS), a tool specifically designed to harvest confidential data from macOS devices.
Technical Analysis of GrassCall.exe/ VibeCall.exe:
VibeCall.exe is a 64-bit executable file that acts as an installer but is malicious in nature. Upon execution, it attempts to install and deploy the Rhadamanthys malware. Rhadamanthys is a sophisticated information-stealing Trojan designed to harvest sensitive data, including login credentials, financial information, and system details.
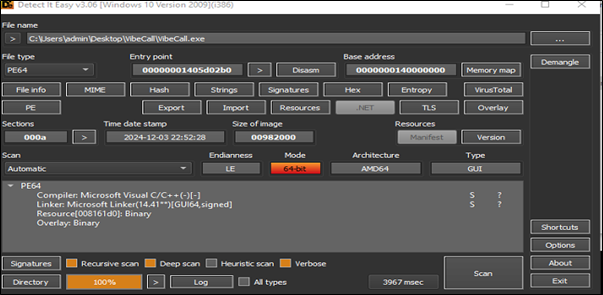
Upon execution, it runs the Add-MpPreference command to add an exclusion path in Microsoft Defender. Specifically, it excludes the entire C: drive, causing Defender to completely bypass all files and folders on C: during its scans. This effectively disables Defender’s ability to detect or respond to any malicious activity occurring within the excluded drive.
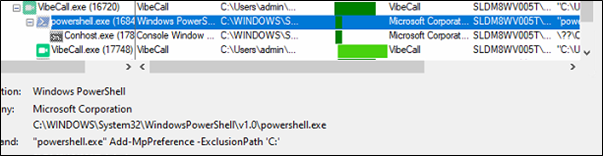
It tries to download multiple Rhadamanthys malware samples and tries to execute it.
hxxp[:]//rustaisolutionnorisk[.]com/downloads/contry_solution_vibecall_e.exe 4b371777c2c638c97b818057ba4b0a2de246479776eaaacebccf41f467bb93c3
hxxp[:]//rustaisolutionnorisk[.]com/downloads/aisolution_vibecall_a.exe f2e8f1f72abbc42f96c5599b8f27f620d91ae1680aa14b4f0bbf3daabd7bee30
hxxp[:]//rustaisolutionnorisk[.]com/downloads/soundsolution_vibecall_c.exe d23f79f9b7e1872d4671a18aa85b810c0cec2e0f5ce07c2cf99ed39f8936c8fb
hxxp[:]//rustaisolutionnorisk[.]com/downloads/videosolution_vibecall_b.exe 386b61ccdd4b785c835a064179d5fa58dc0d5fe34970a04487968e1ee0189ce6
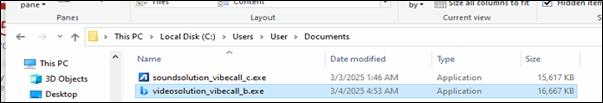
It drops the downloaded samples in C:/Users/user/Documents folder and tries to execute it.
Analysis of Rhadamanthys malware
Upon analysis of one of the Rhadamanthys malware (videosolution_vibecall_b.exe) from the above we found that it is a 32bit packed sample which contains shellcode.
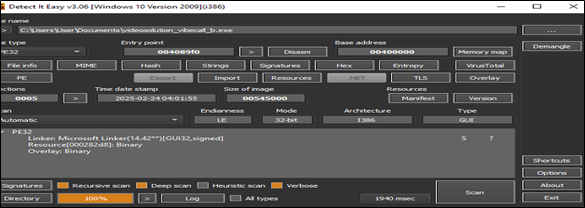
Upon unpacking we found the 2nd payload of Rhadamanthys malware as shown in below fig.
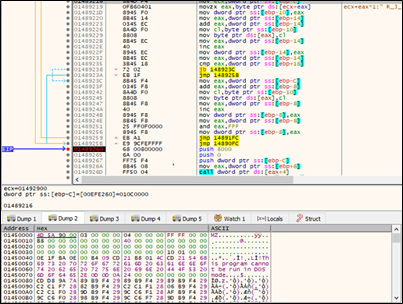
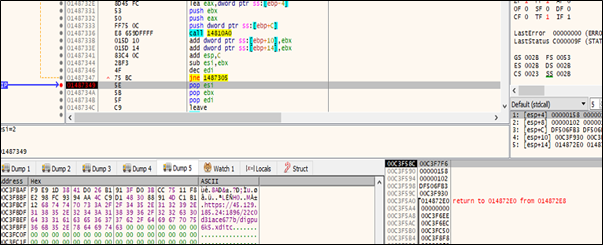
2nd Payload
sha256: 0160c14c3d84dcc5802a329a4d4bedcabd23b3a7761c1cd95d16bd0b7a7bb8eb
The second payload contained a configuration file that attempts to establish a connection to a command-and-control (C2) server. The connection is directed to the URL:
hxxps://45.129.185.24:1896/22c0d31ace677b/digpu6k5.xditc
TTPS:
| T1566.002 | Phishing: Spearphishing Link |
| T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols |
| T1102.001 | Web Service: Social media |
| T1199 | Trusted Relationship |
| T1105 | Ingress Tool Transfer |
| T1059.001 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell/Windows Command Shell |
| T1204.002 | User Execution: Malicious File |
| T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| T1056.001 | Input Capture: Keylogging |
| T1567 | Exfiltration Over Web Service |
| T1566.001 | Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment |
Preventative Measures:
- Verify Job Opportunities: Always confirm the authenticity of job opportunities and the companies offering them. Use official and verified channels to validate any recruitment-related communications.
- Exercise Caution with Downloads: Avoid installing software from unknown or unverified sources, particularly when requested as part of unsolicited interactions.
- Install Reliable Security Tools: Utilize reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to safeguard your system against threats.
- Conduct Regular System Checks: Perform frequent scans on your device to detect and remove malware or other potentially harmful files.
IoCs with Detections:
| File Name | Hash | Detection in Seqrite |
| VibeCall.exe | b63367bd7da5aad9afef5e7531cac4561c8a671fd2270ade14640cf03849bf52 | Trojan.GrassCallCiR |
| videosolution_vibecall_b.exe | 386b61ccdd4b785c835a064179d5fa58dc0d5fe34970a04487968e1ee0189ce6 | Trojan.Rhadamanth.S35275351 |
| contry_solution_vibecall_e.exe | 4b371777c2c638c97b818057ba4b0a2de246479776eaaacebccf41f467bb93c3 | Trojan.Rhadamanth.S35275351 |
| aisolution_vibecall_a.exe | f2e8f1f72abbc42f96c5599b8f27f620d91ae1680aa14b4f0bbf3daabd7bee30 | Trojan.Rhadamanth.S35275351 |
Autors:
Soumen Burma
Dixit Ashokbhai Panchal




